Learn about refractive errors: myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism and presbyopia
16/01/2026
15/05/2023
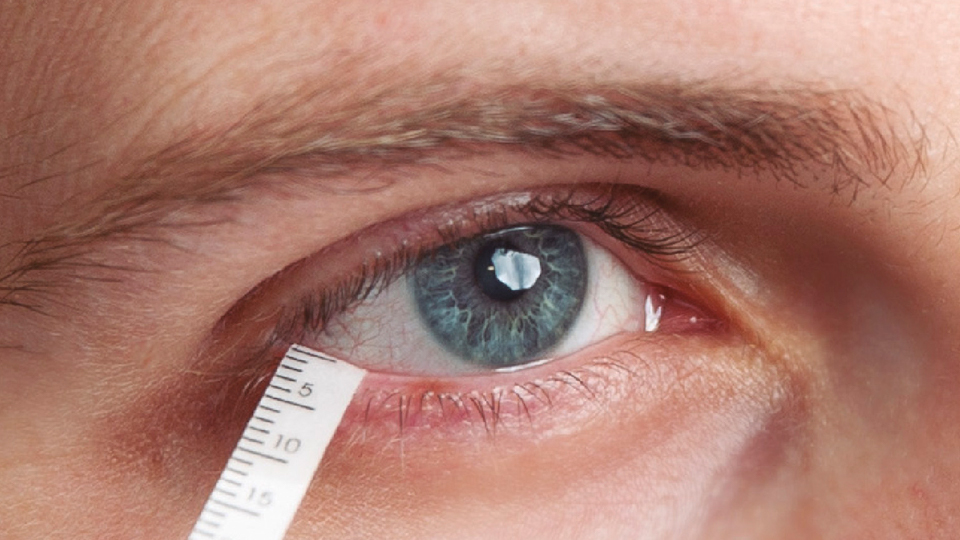
Tears are produced by glands located in our eyes and spread over the ocular surface through blinking. The Schirmer test measures the total production of tears, including both basal and reflex tears. Basal tears serve the purpose of lubricating, nourishing the eye, and protecting the cornea. Reflex tears are produced when an external agent invades our eyes.
It is a simple diagnostic test performed by placing a strip of absorbent paper at the temporal edge of the lower conjunctival sac. This strip remains in the patient's eye for 5 minutes or until it is completely moistened, if that occurs within a time frame shorter than 5 minutes.
If the result exceeds 10 mm, the patient receives double anaesthetic drops, followed by a 10-minute interval before repeating the test. This method prevents any potential stimulation caused by the paper strip and yields the measurement of the eye's basal tear secretion. This measurement is instrumental in determining the presence of ocular pathology and and the appropriate treatment.
Olga Riera and Antonio Beltran, Department of Ocular Biometrics.